Domain Name System (DNS) is an internet service. It translates the domain names into IP addresses. It has two components::
- DNS Server.
- DNS Client.
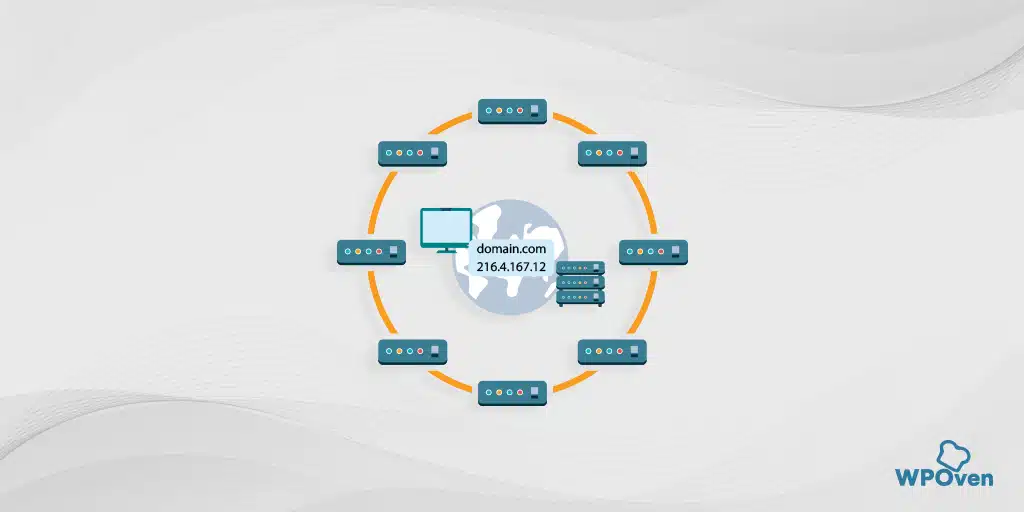
The DNS server works as a global directory of Internet. They are also known as the equivalence of a phone book. Their functionality is to maintain a directory that comprises domain names and then to translate them into internet protocol (IP) addresses whereas a client’s function is to request for a host name which the server has to translate.
There are different types of DNS records. Although our main topic of discussion is AAAA records, we will briefly discuss some other types as well.
A record:
It is the most important and the basic DNS record type. It maps a hostname to a 32-bit IPv4 address. The A in this signifies address. A browser queries on a DNS server by using this record to look up for a website. Not all computers require having an A record, but it is necessary for those systems that provide shared resources on a network. The creation of an A record is simple; all you need is to right-click a zone from the left list of DNS Records Windows. A pop-up menu will appear. Select “New A-record” from the given option and it is created.
CNAME Record:
It stands for canonical name record. It is used to specify a certain domain name that is an alias for another domain. For example, if there is a server where all your images are kept online, you might access it through imgs.abc.com. But, you may also want to access it through images.abc.com. Adding a CNAME record will enable the content to be seen through both the servers.
To use this type of record, select CNAME from the Add Record menu. Enter the hostname and fully-qualified domain name which you would like to alias to.
PTR Records:
PTR stands for pointer records. They are considered to be the opposite of an A record as these are used in reverse lookups. Consider the following example:
To make this ip 192.168.1.1 resolve to www.example.com, the PTR record will look like:
1.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa PTR www.example.com.
This type of records is effective if your website has its own IP address, and it can be configured by the root user who is the server admin.
NS Records:
This kind of server record is a specialized server which handles questions or queries about the location of a domain name’s various services from our local system. It helps to ensure that all your domains on your servers are available all the time. If you have multiple NS records configured, it will make easier for your customers as they will be able to visit your website without any problem. For example, if the area your business is located gets hit by the natural disaster which will lead your web servers to be down, the NS records that you have configured will point to that additional name server that is hosted at some other location. The customers will be able to visit your website without any trouble.
AAAA record:
Also known as Quad-A record, AAAA record maps a hostname to IPv6 similar to an A record, which maps a hostname to ipv4. The difference between both the IP versions is that IPv4 addresses are 32 bits whereas IPv6 addresses are 128 bits. AAAA record is defined in RFC 3596.
Read on to know more about AAAA record in detail:
Name: It is the host for your domain. It is actually a computer within your domain.
TTL: Time to live, it is the time period for which your record will exist in the cache on those systems that have requested your records. It is recommended to set a lower TTL to get the maximum traffic, as the lesser amount it stays in the cache, the more the client will request for your record. An ideal TTL is 1800 seconds or less.
Configuration:
An AAAA record is structured and configured the same way as an A record, but it is comparatively larger. The resource record type value for this record is 128. Eight groups of 16-bit values like fe80::223:16ff:fed2:cc2a are used to notate AAAA records.
Let’s have a look how it works:
The most widely used domain name server BIND is used to configure the DNS records. If you have multiple addresses that are defined with the same name, the queries will be responded by BIND with a list of addresses but the order may change. It depends on the value of the rrset-order statement that is located in BIND’s named.conf file. A same ip can be defined with different names. It is not necessary for IP addresses to be in the same subnet or to use the same routine prefix. To prevent unintentional duplicate definitions, it is advisable to arrange the AAAA record in either an ascending or descending order. There is no terminating dot because IPv6 is not a name but an address.
For Example:
Name: www.abc.com
TTYL: 1800
TYPE: AAAA
DATA: 2600:1800:5::10
In the above example, www.abc.com. Is the host for which an entry is being made. The IPv6 address is 2600:1800:5::10. And the TTL shows for how much duration the record will stay in the cache of the system.
To get more understanding about AAAA record, we need to know more about IPv6.
IPv6:
IPv6, also known as IPng (Internet Protocol Next Generation), is the latest Internet Protocol version. It is the successor to IPv4. It allows the internet to have a steady growth in terms of the amount of data traffic transmitted and the number of hosts connected. Its main benefit over IPv4 is that it has increased the pool of addresses. There are several other technical changes in IPv6 to improve the internet protocol. Some of these are:
- Simpler header format.
- Simplified and more efficient routing.
- Flow labeling.
- No more Network Address Translation.
- Auto-configuration.
- Better multicasting routing.
It is important to add IPv6 in your existing infrastructure and also make sure to use the same data in IPv4 and IPv6 to address the queries.
Difference between IPv6 vs IPv4

I am a Co-Founder at WPOven INC currently living in Vancouver, Canada. My interests range from Web Development to Product development and Client projects. I am also interested in web development, WordPress, and entrepreneurship.





![How to Fix Error 523 "Origin Is Unreachable"? [Solved] Error code 523](https://www.wpoven.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Error_523.png.webp)

