Hackers always devise new ways or invent new methods to hack or attack a website. You also might have often heard the term DNS poisoning or DNS spoofing, which is considered quite a popular cyber-attack strategy. After all, it is one of the easiest and most clever cyber-attack strategies that cannot be easily detected.
Basically, DNS poisoning or also known as DNS cache spoofing or DNS spoofing, whichever you like to call it, is one of the most deceptive cyber-attacks in which hackers cleverly redirect the web traffic of a website to another malicious website or a Fake web server. OR the hackers can simply restrict the visitors to load the spoofed website.
These Malicious or Fake websites impersonate the actual website and make it an easy path for hackers to steal visitors’ sensitive information such as credit card information, Bank details, passwords, or personal information.
While visiting a Fake or spoofed website, a visitor might not notice anything fishy. The website might look normal just like the original one and even function normally, that seems everything seems safe.
Or, in another case, the visitors might find it difficult to reload the spoofed website unaware of the fact that the site has been hacked. They keep on trying to reload the website a time or more and out of frustration blame the web hosting company.
The best way to tackle DNS poisoning is prevention. This article will try to explore every term related to DNS poisoning, that must know and also share some of the best methods to prevent it from happening.
So, keep reading this article to the end and learn everything about DNS poisoning in a very comprehensive way. Let us get started!
What is DNS poisoning aka DNS Spoofing?
As we have already discussed in the introduction section that DNS poisoning is another type of cyber-attack, in which a hacker basically impersonates a website exactly like the original website and make it easier for them to steal the sensitive information of the visitors.
This impersonation of a website is generally done in order to carry out online phishing or interrupt the normal flow of web traffic.
The hackers are able to carry out this hacking technique by finding out the loopholes within the Domain Name Systems (DNS). When they successfully figure out all the loopholes or vulnerabilities, they redirect the web traffic from the original website to the fake one.
If you do not know anything about the term DNS or don’t know how it works? Please check out our dedicated article on ” What is DNS? How does a domain name work? ” And learn all the various terms associated with it and its functionality in a very comprehensive way.
To better understand this, let us consider an example. Suppose someone has asked for your home address but you do not want them to come to your place, instead you provide them with a fake address. To make things look real, you went on to that Fake address and change all around the street and house numbers. So that, without any doubt they can actually end up at the wrong house or destination.
How does DNS Poisoning Work and What Causes it?
The whole mechanism of DNS poisoning revolves around the basics of How the internet works and how it is able to route users to their destination websites.
Like your home addresses or any location on earth has unique coordinates, every device and server has its own unique and distinct IP addresses, which is the same analogy as our physical home addresses. These IP or Internet protocol addresses are basically a series of numbers that are connected to every device on the network and use Internet protocol for communication.
Every website you visit has a distinctive domain name that helps internet users easily remember and identify them in the front end. But in the backend things work differently, when a user enters the website URL or address in the browser’s address bar, the DNS or Domain name server immediately maps the domain name to its proper IP addresses and routes the traffic.
Now, at this point, hackers took the advantage of all the vulnerabilities and loopholes to redirect all the web traffic to a Fake website. Actually, hackers infiltrate a DNS server and make some changes to its directory that point users to a different illegitimate IP address. This process is technically known as DNS poisoning.
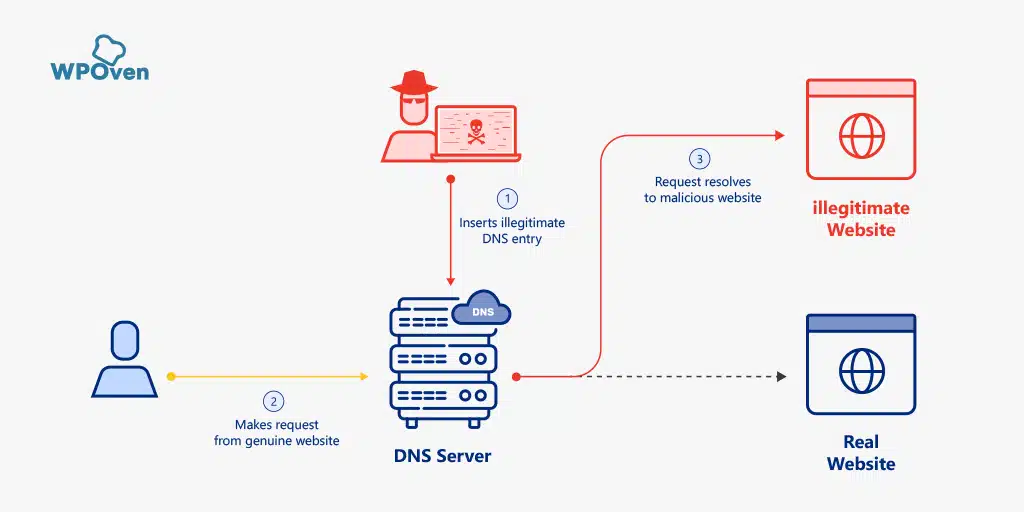
After hackers were successfully able to infiltrate the DNS server and able to point web traffic to the illegitimate website, this redirecting part is known as DNS spoofing. Got confused between DNS poisoning and DNS spoofing? Don’t worry, all your doubts will be cleared up in the next section.
Now it is not the end, the DNS cache poisoning takes this whole process one step further. After the completion of DNS poisoning, the user’s browsers store the fake website’s IP address in its cache memory.
As a result, whenever a user tries to visit the original website, it will automatically redirect to the Fake one, even though the problem has been fixed. But how is it possible? Are there no security protocols? Let us find out.
You might have also heard about DDoS attack which is quite similar to DNS Poisoning, check out this post on ” A complete guide on DDoS attack” and learn more about it.
Why does DNS Cache Poisoning happen?
One of the biggest reasons that allow this DNS cache poisoning to happen is the entire weak system of routing web traffic. DNS servers use UDP or User Datagram Protocol in which there is no need for verification of information required between the sender and recipients during the communication.
Whereas in TCP or Transmission Communication Protocol, you will find both sender and the recipients are required to perform a handshake to start the communication and also do the device identity verification.
Therefore, this UDP arises an opportunity for hackers to send a message through it and pretend it’s a response from a legitimate server by using a Fake identity. Since there is no additional verification facility available, if the DNS resolver receives a fake response, it will accept and cache the data without any doubt.
Despite the fact that DNS caching process has too many flaws, loopholes, or vulnerabilities present. Doing DNS poisoning attacks is not as easy as it seems. To make this happen, a hacker has to quickly send a fake response within a few milliseconds, right before the response from the legitimate nameserver kicks in.
DNS Poisoning vs DNS Spoofing
You might have seen; both the terms DNS poisoning and DNS spoofing are considered to be the same and often used interchangeably. But there is a slight difference between these two:
- DNS poisoning– It is a process or method by which hackers or attackers infiltrate DNS and make certain changes to the information in order to redirect the web traffic to an illegitimate website.
- DNS spoofing– Whereas, in DNS spoofing is the end result of DNS poisoning, where the traffic is being redirected to the malicious website due to the DNS cache poisoning.
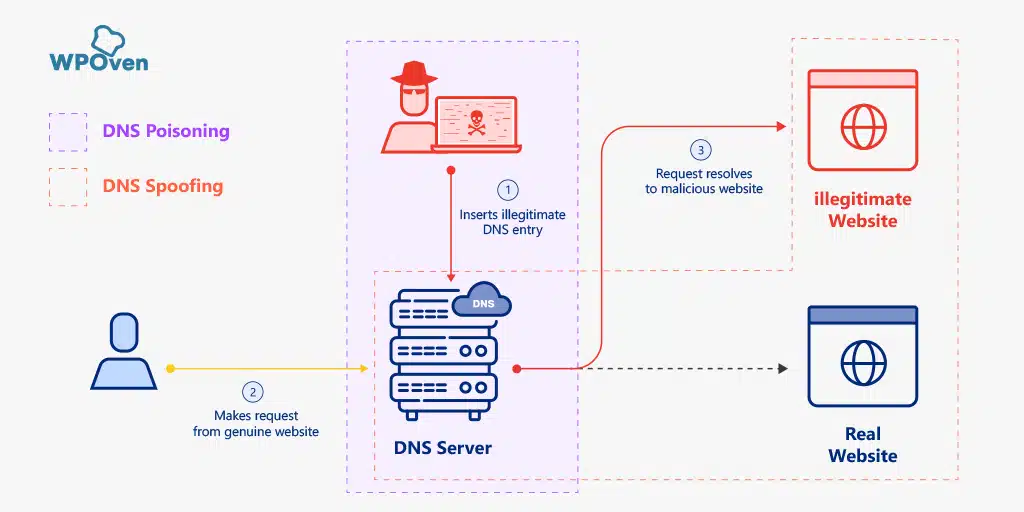
In other words, we can say DNS poisoning is the process and the DNS spoofing is the end result.
What are the biggest threats due to DNS Poisoning?
DNS poisoning is one of the most notorious attacks that can potentially damage anyone or any organization. It is so severe that once you fall victim to it, then it becomes very difficult to detect and fix the issue.
It is because, after DNS poisoning, the worst thing that happens to any device is DNS cache poisoning, which is very difficult to fix because, the user will be automatically by default redirected to the malicious website again and again.
In addition to that, it is also very difficult to either suspect or detects DNS poisoning, especially in the case where hackers redirected your website traffic to an impersonate fake website that looks exactly the same.
As a result, the viewers without any doubt input their critical information as normal and put themselves or their organizations at high risk.
Critical information theft
DNS poisoning allows hackers to redirect your website traffic to a fake one impersonating exactly yours and stealing visitors’ sensitive information like credit card details, log in and password credentials, bank details, or security keys, etc.
Infecting Devices with Viruses and malware
Once the hackers are able to redirect your website traffic to their malicious and illegitimate impersonating website, they will also be able to infect visitors’ devices by installing malicious software or hosting viruses on them. This can lead to multiple other wrongdoings, such as infecting other devices they contact and also letting them steal their sensitive information.
Blocking Security Updates
Hackers can also use DNS poisoning to redirect traffic from security providers and block them to gain regular security updates and patches. This type of attack has a long-term effect and can be severe resulting in weakening overall website security and they will be more prone to other types of attacks such as viruses and malware.
Government restrictions
Apart from some serious threats, DNS poisoning can also benefit the Government in terms of restricting or banning certain critical information to be accessed in the public domain. With the help of this technique, the government can control its citizens by banning them from visiting certain websites that they are not meant to see, such as Dark websites, military information, etc.
How to Prevent DNS Poisoning?
It is always truly said that “Prevention is better than cure” and also it can cost you a lot more to fix an issue than to prevent it. After all, once your device gets caught in DNS poisoning and your website goes down, the visitors won’t blame hackers for this, but they will directly blame you or your company.
Although prevention is necessary for DNS poisoning to happen it is not that easy, let’s see what you can do from your side.
Use a reputed and secured web hosting
Choosing a reputed and secure web hosting from the very beginning is always encouraged and one should never compromise on that. Since there are plenty of web hosting service providers out there, you should choose the only one which has a good reputation and the best security features in the industry.
WPOven is one of the renowned and reputed Web hosting service providers in the US, that believes in providing a great web hosting experience. All the websites hosted on WPOven are provided with enterprise-level security and other features that nobody can provide at affordable rates. Some of the top-notch security features of WPOven that you should never miss are:
- Free Let’s encrypt-based SSL for all your sites
- Hardened Servers
- Web Application Firewall
- Built-in Bot protection
- Regular Anti-malware scanning
- 24X7 WordPress Expert support
- Worldwide Cloudflare integration
- Unlimited Staging
- Daily offsite backup and 1-click restore
- Anti-hacking support
- Automatic and safe updates, etc.
To learn more, you can also check out our dedicated page on ” Highly secure WordPress hosting“.
Enable DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC)
Enabling DNSSEC can be one of the most important steps that will help you to prevent DNS poisoning or DNS spoofing. The DNSSEC adds up a layer of authentication that is lacking in your typical Internet protocols for verifying DNS data.
Use built-in protection DNS software
Some of the DNS software comes up with built-in protection features, you must talk to the developers and confirm the same before installing it.
Keep Your system Up to date
It is always recommended that you must keep your system up to date with the latest versions or definitions available. Similarly, your DNS also needs to be updated regularly, which often adds new security protocols, and bug fixes and removes previous vulnerabilities. In addition to that, the latest updates also allow you to be ready for future changes.
Restrict DNS requests
Restricting or limiting DNS requests to open ports will help you to avoid flooding with requests, that can possibly infect your data.
Always enable Data Encryption
Enabling Data encryption in DNS requests as well as replies can also be beneficial to prevent DNS poisoning. This adds up an additional layer of protection through which it becomes difficult for hackers to intercept the data and continue wrongdoings.
For instance, by any chance a hacker is able to infiltrate into your DNS and manage to intercept that data, they still won’t be able to do anything. It is because since the data is encrypted, it won’t be readable and hackers won’t be able to use that particular information to impersonate the original website.
How to Detect DNS Poisoning?
Now, if you would like to check whether your website has been a victim of DNS poisoning or not, you have to check the following:
- An unexpected drop in your website traffic can be a sign of DNS poisoning because all your website traffic will be redirected to an illegitimate website.
- Try to access your website from another device or use a VPN and see if your website is redirected to an unfamiliar website or not. If yes, it means your DNS cache has been poisoned.
- If you notice suspicious DNS activity found on a domain, whether it is from a single source to single domains or multiple domains.
Read: 🚩 chrome://net-internals/#dns – How to Clear DNS Cache Chrome
Different Approaches to Fix DNS Poisoning
As for now, you have been aware of how DNS poisoning happens, what are its possible threats, its preventive measures, and how you can detect it. But if you are unfortunate enough, and your website becomes a victim of DNS poisoning, then How you can fix it? Let us check some of the methods that can help you to deal with it.
Run antimalware program
If you are able to detect DNS poisoning the first thing you need to do is to make sure there is no malware infection that has been taking place. To ensure that, run an antimalware program and see if it is able to detect it and solve the issue. However, some of the antimalware programs still cannot detect and fix the DNS poisoning issue, therefore you cannot completely rely on that.
You must also keep in mind that every malware infection works differently and hence requires a different approach to fix them.
Manually fixing DNS poisoning
If antimalware doesn’t work for you, the second method you can try is doing it manually. For that, the first thing you need to do is to turn off your Internet device (Wi-Fi) completely or unplug any PC’s network cable. So, the PC will not be able to download any further malicious code while you are trying to fix the issue.
When you have successfully disconnected your device from any network source, it is time to get started. The whole DNS poisoning mechanism is based on redirecting the Windows name resolution process.
In reality, the Windows OS itself uses multiple name resolution mechanisms, in which the majority of them are just residue from the initial days.
This is how Windows name resolution works. When windows try to resolve a name, the first thing it does is to check whether the name is not its own, after that it proceeds to check the Hosts file. Checking the host file is mandatory because it is one of the most popular targets for hackers to attack.
In case Windows isn’t able to resolve the hostname via the host file, it will have no other choice but to use DNS. Even though the DNS also doesn’t work, Windows OS will use NetBIOS as its last option.
Since the whole name resolution mechanism is managed and controlled by the Windows registry. It is highly recommended that you should take a backup of your device first and then proceed to edit the registry. It is because by any chance if anything went wrong it could possibly damage your whole OS.
Now open Registry Editor, you will find it in your Windows OS by simply searching in the menu bar as shown in the picture below.
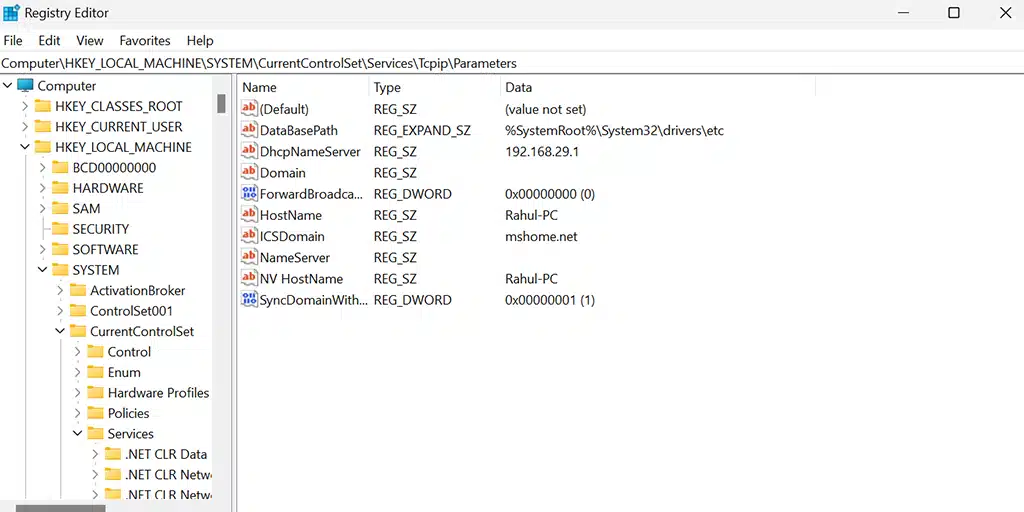
Now in the Registry Editor go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Services > Tcpip > Parameters. As we have previously said, windows initiate the name resolution process by checking whether the hostname is it’s own or not. So, in the HostName key, you will find the system’s hostname is being stored as shown below.
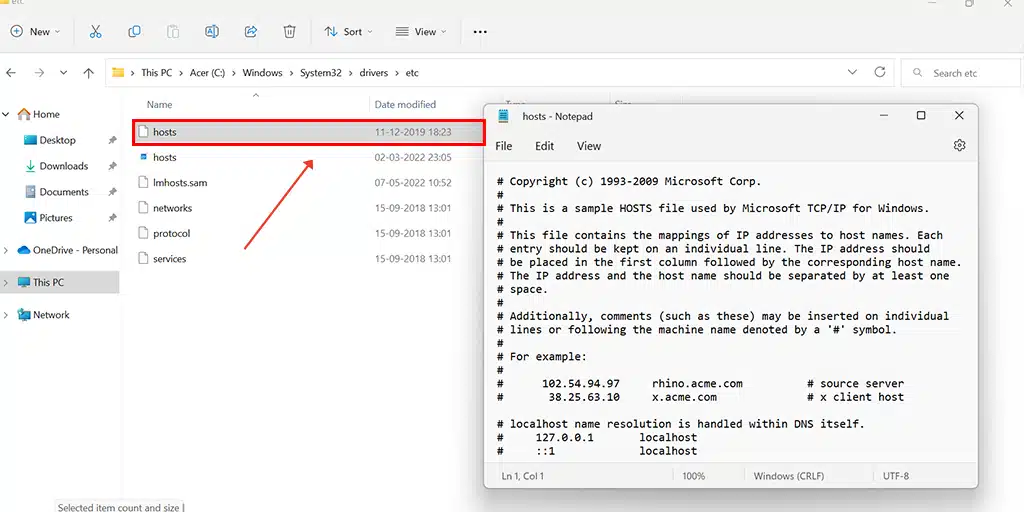
Now after checking the HostName, in the next step, the operating system does is to check the Host file. Windows 10 as well as 11 users, can find the location of their host file at C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\etc. By default, every comment mentioned in the host file should be starting with a pound (#) sign unless you made certain changes to it.
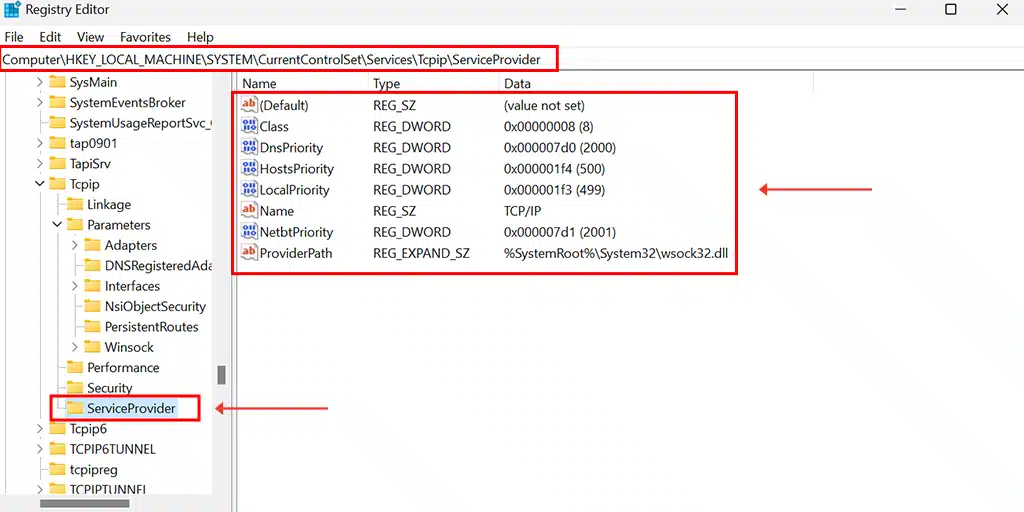
As we have earlier discussed the whole name resolution mechanism and its order is being managed by the registry itself, you can check and verify the order by going to the location HEKY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\ServiceProvider in the registry editor.
Now, you can see there are different entries available such as Dns Priority, HostsPriority, LocalPriority, and NEtbtPriority. Each of them has been assigned a unique number representing their priority hierarchy. The higher the numeric value, the lower the priority, and vice versa. Therefore, LocalPriority with an assigned numeric value of (499) shows higher priority than the HostPriority with a (500) assigned numeric value.
If you do not like to go much deeper into it, there are two main things you can do from your side. The first thing to examine and verify your IP address configuration is to make sure your device has not been using an illegitimate DNS server.
The second thing you can do is completely flush your DNS cache, in order to get free from any potential suspicious entries. To do this, all you need is to open a Command prompt on your windows PC and follow the simple steps given below:
Here are the steps to clear windows to flush DNS –
- Go into Command prompt mode:
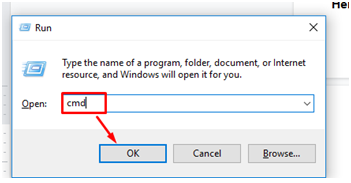
- A. Press Windows + R buttons on your keyboard
- This will launch a small box for Run Commands.
- Enter CMD in the box and press enter
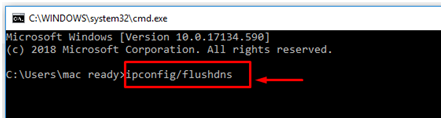
- It will open Command Prompt Screen
- Enter ipconfig/flushdns and press enter as shown below
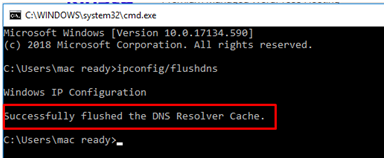
- It will display the Success Message as confirmation of DNS Flush
There is no distinctive rule for fixing a DNS poisoning infection. Each and every infection is different from another and requires different approaches to tackle them. But for any infection, you must try to fix it with an antimalware program first before moving to the manual method.
DNS Poisoning Examples
There are plenty of DNS poisoning cases have been reported in which some of the high-profile cases are mentioned below:
As per the reports by the renowned US tech news publication The Register, in 2018, the Amazon AWS network has been hijacked by a group of thieves, who steal a chunk of cryptocurrency from MYEtherWallet.
The group of thieves managed to infiltrate the AWS network and conducted DNS poisoning due to which they were able to redirect all the traffic from the domains hosted on the network to a fake impersonating website.
One of the major victims of this attack was the famous cryptocurrency website Myetherwallet.com. The thieves were able to redirect all the traffic of myetherwallet.com to a malicious website masquerading as the real website and stole all the sensitive information such as the login credentials of the visitors.
As a result, the thieves used this information to log in to their actual myetherwallet accounts and drain out all the funds.
It has been estimated that the bandits managed to transfer about $17 million in Ethereum to their own wallets over time.
Summary
DNS attacks are no longer new and have been prevailing for quite a long time. The best way to tackle such attacks in the future is to follow strict and strong preventive measures rather than looking for a solution.
It is because these types of attacks are very tough to detect and every infection can be different from others, Hence the solution is not fixed. The best thing you can do from your side is to host your website on a reliable, trusted, and reputed web hosting website and enjoy peace of mind.
If you would like to add some points to it or have any doubts, please do let us know in the comment section below.
Choosing the right web host can be your boon to save you from all the Hacker attacks, Security threats, website handling issues, and many more. You can experience complete peace of mind web hosting services by hosting your website on WPOven’s Highly secure, reliable, and Fastest dedicated servers. You will be provided with,
- Free Let’s encrypt-based SSL for all your sites
- Hardened Servers
- Web Application Firewall
- Built-in Bot protection
- Regular Anti-malware scanning
- 24X7 WordPress Expert support
- Worldwide Cloudflare integration
- Daily offsite backup and 1-click restore
- Anti-hacking support
- Automatic and safe updates, etc.
You can have all these features and much more in a single plan starting at $16.61 per month with unlimited Free migrations, unlimited staging, and a 14-day risk-free guarantee, Signup Now!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if my DNS is poisoned?
There are some ways through which you can detect or check if your DNS is poisoned or not.
1. Check if there is any unexpected drop in your website traffic
2. Monitor your DNS for suspicious activity
3. Try to access your website from another device or use a VPN and see if your website is redirected to an unfamiliar website or not.
What are the most common DNS attacks?
The most common DNS attacks are:
1. DDoS attacks
2. DNS spoofing
3. DNS flooding
4. NXDOMain attack
5. DNS tunneling, etc.
Why do hackers use DNS poisoning?
Hackers use DNS poisoning to conduct DNS spoofing due to which all the web traffic will be redirected to another impersonating fraudulent website. This type of attack opens the door for hackers to steal visitors’ sensitive information or disrupt web traffic.

Rahul Kumar is a web enthusiast, and content strategist specializing in WordPress & web hosting. With years of experience and a commitment to staying up-to-date with industry trends, he creates effective online strategies that drive traffic, boosts engagement, and increase conversions. Rahul’s attention to detail and ability to craft compelling content makes him a valuable asset to any brand looking to improve its online presence.